Autoimmune Neurological Disorders
Multiple Sclerosis
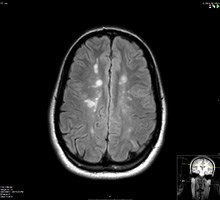
Multiple sclerosis or MS is an immune-mediated disorder in which the patients’ own immune system attacks their brain and/or their spinal cord causing inflammation and scarring. It commonly manifests in the form of relapses and remissions but some forms of the disease are progressive. It can cause variable neurological manifestations and it usually affects young adults. Early and prompt treatment can prevent relapses and slow down or prevent disability. Learn more about multiple sclerosis.
Transverse Myelitis
Transverse myelitis is an immune-mediated inflammation of the spinal cord that can occur as a single isolated event or as part of MS, neuromyelitis optica, or other disorders. Isolated myelitis resolves or improves partially in two thirds of the cases but it increases the risk of developing MS in the future and is an indication for regular neurological monitoring. Learn more about transverse myelitis.
Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is an immune-mediated inflammation of the optic nerve leading to painful partial loss of vision that is often temporary. Isolated optic neuritis increases the risk of future MS and is an indication for regular neurological monitoring.
Neuromyelitis Optica
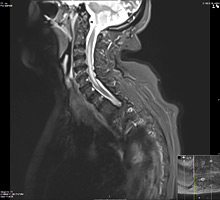
Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) or Devic’s disease is a severe autoimmune inflammatory condition that preferably involves the optic nerves and the spinal cord causing extensive inflammation and tissue damage. It is caused by specific antibodies against water channels in the central nervous system and often leads to significant disability if not treated aggressively and in a timely manner. NMO is more common in African American and Asian populations and is not uncommonly misdiagnosed as MS which can lead to improper and potentially harmful treatment. Learn more about Neuromyelitis Optica.
An MRI image showing a long area of inflammation in the spinal cord in a patient with NMO.
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is usually a single occurrence of severe inflammation of the brain and/or the spinal cord following a viral infection or vaccination. Unlike MS, ADEM causes acute mental confusion along with other neurological symptoms like seizures, difficulty speaking, weakness, etc.
Autoimmune or Paraneoplastic Encephalitis
Autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) is an autoimmune condition in which specific antibodies or pathogenic immune cells attack the brain causing confusion, seizures, movement disorders, and other symptoms. In some patients, AIE can be associated with existing or developing cancer.
Rare Neuroimmunological conditions
These include conditions like neurosarcoidosis, stiff person syndrome, Susac’s syndrome, Behcet's disease, CLIPPERS, IgG4 associated neurological disease, hypertrophic pachymeningitis, steroid-responsive encephalopathy associated with autoimmune thyroiditis (SREAT) or Hashimoto’s encephalopathy, among others.
Spasticity
Spasticity is an abnormal increase in muscle tone secondary to any pathology affecting the motor tracts in the brain or the spinal cord. It leads to body stiffness and spasms causing problems with motor function, comfort, ease of care, and personal hygiene. Common causes of spasticity include MS, myelitis, stroke, traumatic brain or spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and some hereditary conditions.


